- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2025-11-10 at 2:52 pm #5401
You can usually read most RFID chips from a few centimeters to 15 meters, depending on the RFID chip range of the system you use. Many important factors affect how far an RFID chip can be read. These include the antenna type, tag position, reader power, cable quality, and the area around the chip. MarktraceRFID provides smart solutions to optimize these elements, ensuring that the chips perform reliably every time.
Factor
Impact on Read Range
Antenna Selection
Stronger antennas let you read farther
Tag Positioning
Where and how you place tags matters
Reader Settings
Power and sensitivity are very important
Cable Selection
Good cables make signals stronger
Environment
Metal and water can make range shorter
Key Takeaways
-
RFID chip range can be very short or very long. It can go from a few centimeters up to 15 meters. The range depends on the system and how it is set up.
-
Many things can change how far RFID can read. These include the antenna type, where the tag is placed, how strong the reader is, and the environment around it.
-
There are different types of RFID. Each type has its own range. For example, UHF RFID works well for shipping. It can read tags from farther away.
-
Active RFID systems can read tags from very far away. They can work from hundreds of feet away. This makes them good for big spaces.
-
To make RFID work better, pick the right tag. Put the tag in a good spot. Use strong antennas to help the system.
-
Things like metal and water can make RFID range shorter. Think about these things when you set up your system.
-
Test your RFID system often. This helps you find and fix any problems with range.
-
Talk to experts to help you pick the best RFID system. Make sure it fits your needs and your space.
RFID Chip Range Overview
RFID chip range is how far a tag can talk to a reader. This distance is important for tracking things or checking inventory. If you work in shipping or asset tracking, you need the right range. It helps you cover big spaces and keep good records. MarktraceRFID gives you choices that fit what you need. You can pick long-range or strong performance in hard places.
Typical RFID Read Distances
Different RFID types have different ranges. The table below shows how far each type can read:
RFID Type
Read Distance
Passive Microwave
~15 feet
Semi-Passive Microwave
~100 feet
Active Microwave
~350 feet
Low Frequency (LF)
3-5 feet
High Frequency (HF)
1-3 feet
Very High Frequency (VHF)
1-1000 feet
Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
1-30 feet
Microwave Frequency
1-300 feet
You can see the range differences in the chart below:
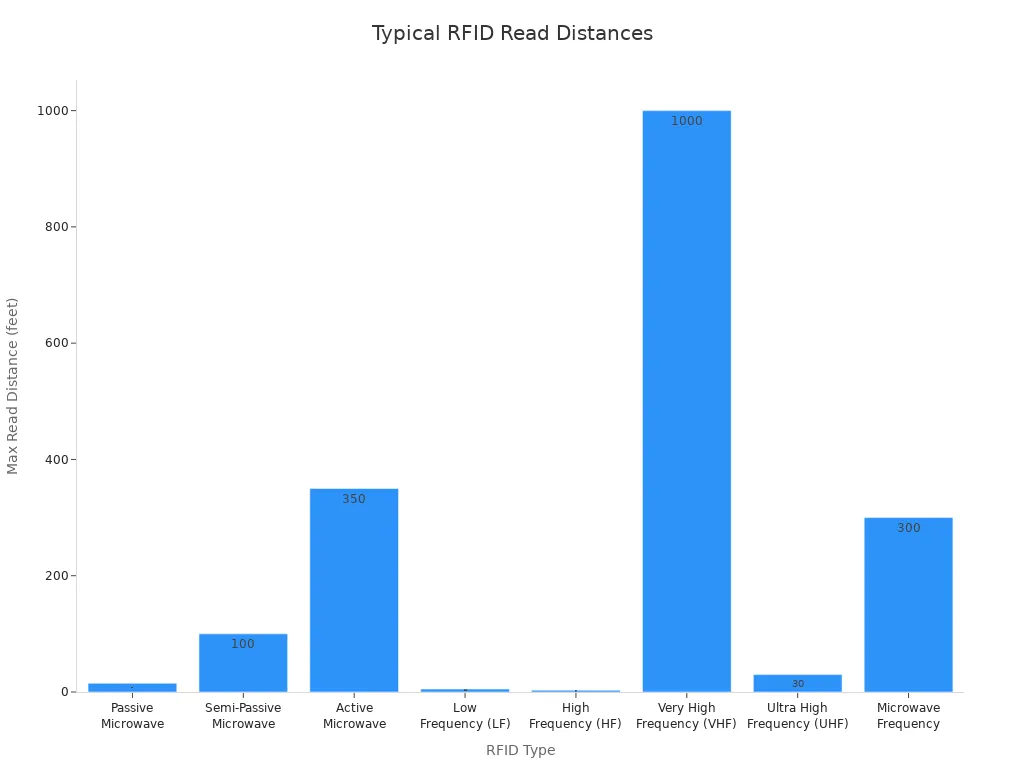
Pick the RFID type that works best for your job. UHF RFID is good for shipping because it reads tags far away. HF RFID is better for close-up uses like door access.
Maximum Range for RFID Chips
You might ask how far RFID chips can go. The answer depends on the type and setup. Here are some examples:
-
Long-range readers in warehouses can reach 8–15 meters.
-
Some special models can go up to 20 meters.
-
HF readers reach about 18 inches.
-
Active RFID systems can read tags from 1,500 feet away.
-
Passive UHF handheld readers reach about 10 feet, but some can go up to 600 feet.
If you need to cover a big area, active RFID gives the longest range. MarktraceRFID lets you change the range to fit your project.
Factors Influencing RFID Chip Range
Many things change how far you can read an RFID chip. Pay attention to these to get the best results:
Factor
Description
Orientation
Turning the tag changes how well the reader gets the signal.
Read Angle
The angle between reader and tag matters; good placement helps.
Tag Placement
Putting tags on metal or near water lowers the range.
Tag Type
Active tags read farther than passive ones.
RFID Frequency
Higher frequencies usually mean longer ranges.
Reader Strength
Stronger readers reach farther.
Reader Power Settings
Changing power and sensitivity helps you get the best range.
Tip: You can make your RFID chip range better by picking the right tag, placing tags in smart spots, and using strong antennas. MarktraceRFID helps you set these up for your space.
MarktraceRFID gives you choices for long-range, low power use, and strong work in tough places. You can trust their systems to work well, even with interference or very hot or cold weather.
Types of RFID Systems

Image Source: unsplash You should know the main types of rfid systems before picking one for your business. Each type uses its own frequency and has a different read range. These systems work in many industries and follow certain rules.
Passive RFID Range (LF, HF, UHF)
Passive rfid systems do not have batteries. The reader gives power to the tag and reads its data. The range changes with the frequency and where you use it.
LF Range
Low-frequency (LF) rfid works at 125 kHz. It can read up to 10 cm away. LF tags are good for tracking animals and letting people in doors. These systems use ISO/IEC 18000-2 rules.
HF Range
High-frequency (HF) rfid uses 13.56 MHz. It can read up to 30 cm away. HF tags are used in libraries and smart cards. ISO 15693 is the main rule for HF systems.
UHF Range
Ultra-high-frequency (UHF) rfid works from 865 MHz to 928 MHz. UHF tags can be read up to 6 meters away. These systems are used in shipping and keeping track of items. EPC Gen 2 (ISO/IEC 18000-63) is the rule for UHF rfid.
Here is a table that shows the usual read ranges for passive rfid systems:
RFID Type
Frequency Range
Possible Read Range
Standard
LF
125 kHz
up to 10 cm
ISO/IEC 18000-2
HF
13.56 MHz
up to 30 cm
ISO 15693
UHF
865–928 MHz
up to 6 m
EPC Gen 2 (ISO/IEC 18000-63)
Note: In Europe, rfid systems must follow ETSI EN 300 220 and EN 302 208. ERO 70 03 sets rules for safe use.
Active RFID and Maximum Range
Active rfid tags are used when you need to track things far away. These tags have batteries and send signals farther.
Battery-Assisted Passive RFID
Battery-assisted passive tags have a small battery to help the signal. They can be read farther than normal passive tags, but still need the reader to wake them up.
Fully Active RFID
Fully active rfid tags send signals by themselves. They can be read from hundreds of feet away. In factories, UHF active rfid tags work from 400 MHz to 3 GHz. These systems can reach 30 meters or even more than 100 meters. These tags are great for tracking things in big places.
-
You can track cars in parking lots.
-
You can watch tools in warehouses.
-
You can check items in outdoor yards.
Microwave RFID Range
Microwave rfid systems use higher frequencies and can read farther. You can track things over many meters or even hundreds of meters. These systems are good for fast-moving things, like toll booths or sorting packages.
Here is a chart that shows how far passive, active, and microwave rfid systems can track:
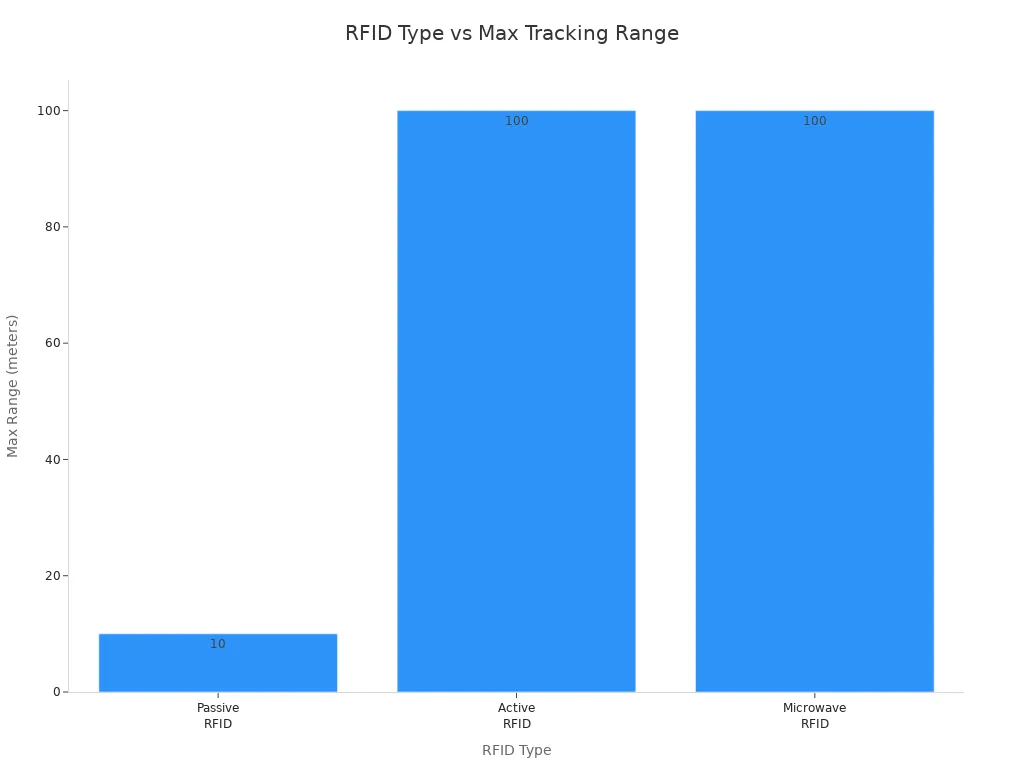
Tip: Pick the rfid system that fits your job and follows the rules in your area. MarktraceRFID has choices that meet world standards and work well.
Technical Specs for RFID Range
Tag Size and Material
You must think about the size and material of your RFID tags. These things change how far you can read the tag. Bigger tags have bigger antennas. This helps the signal go farther. Smaller tags fit on tiny things, but they do not read as far.
The stuff around the tag matters too. Some things, like metal or water, block the signal. For example:
-
Metal can mess up the power between the tag and reader.
-
Water, even in people, soaks up radio waves and makes the range shorter.
-
The coating on the tag can also change how well the signal moves.
Always think about where you will put your tags. If you need to tag hard places, MarktraceRFID has special tags that work well, even in tough spots.
Antenna Design
Antenna design is very important for RFID chip range. The right antenna helps your system work better. Different antennas do different jobs. The table below shows how each one works:
Antenna Type
Design Features
Best Use Cases
Range/Gain
Directional Antennas
Focus RF energy into a narrow beam (30–70° beamwidth)
Linear pathways (conveyor belts)
8–12 dBi (longer range)
Circular Polarized Antennas
Emit waves in a rotating pattern, reducing orientation dependency
Varying angles (pallet racks)
10–15 meters in open areas
Patch Antennas
Compact, flat panels ideal for fixed installations
Indoor/outdoor portals
IP67-rated for durability
Yagi-Uda Antennas
Multi-element directional antennas for extreme range
Rural or open industrial sites
15–20+ meters
Factors to Optimize
Ensure frequency match, polarization, height, and angle for performance
General optimization
Pick the antenna that fits your job. If you track things on a conveyor, use a directional antenna. If you need to read tags at many angles, use a circular polarized antenna. MarktraceRFID can help you pick and change antennas for your needs.
Tip: Make sure your antenna matches your RFID frequency. Set it up right to get the best range.
Reader Power and Sensitivity
The reader is like the heart of your RFID system. Its power and sensitivity decide how far it can read tags. You can change the power on most readers, from 0 dBm to 27–31.5 dBm. More power lets you read tags farther away. But you should watch out for other devices that might cause problems.
Reader sensitivity shows how well it hears weak signals. Higher sensitivity means it can read tags from farther away, even if the signal is weak. The table below explains these things:
Specification Type
Description
Transmit Power
The amount of RF energy emitted by an RFID reader, configurable from 0 dBm to max levels (27-31.5 dBm).
Impact on Range
Adjusting transmit power can significantly change the read distance, with a 3 dBm change halving or doubling the effective power.
Receive Sensitivity
Measures how sensitive the reader is to weak signals, typically between -84 dBm and -92 dBm.
Impact on Detection
Higher sensitivity increases the likelihood of reading tags with weak signals, thus extending effective range.
You should balance power and sensitivity for the best results. https://www.marktracerfid.com/blogs/rfid-chip-range-technical-specifications-performance-guide.html
marktracerfid -
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.

